Bayesian implementation of the MR-Egger multivariate model with choice of prior distributions fitted using JAGS.
Source:R/mr_egger_rjags.R
mr_egger_rjags.RdBayesian implementation of the MR-Egger multivariate model with choice of prior distributions fitted using JAGS.
Usage
mr_egger_rjags(
object,
prior = "default",
betaprior = "",
sigmaprior = "",
n.chains = 3,
n.burn = 1000,
n.iter = 5000,
seed = NULL,
rho = 0.5,
...
)Arguments
- object
A data object of class
mr_format.- prior
A character string for selecting the prior distributions;
"default"selects a non-informative set of priors;"weak"selects weakly informative priors;"pseudo"selects a pseudo-horseshoe prior on the causal effect;"joint"selects a joint prior on the intercept and slope.
- betaprior
A character string in JAGS syntax to allow a user defined prior for the causal effect.
- sigmaprior
A character string in JAGS syntax to allow a user defined prior for the residual standard deviation.
- n.chains
Numeric indicating the number of chains used in the MCMC estimation, the default is
3chains.- n.burn
Numeric indicating the burn-in period of the Bayesian MCMC estimation. The default is
1000samples.- n.iter
Numeric indicating the number of iterations in the Bayesian MCMC estimation. The default is
5000iterations.- seed
Numeric indicating the random number seed. The default is the rjags default.
- rho
Numeric indicating the correlation coefficient input into the joint prior distribution. The default value is
0.5.- ...
Additional arguments passed through to
rjags::jags.model().
Value
An object of class eggerjags containing the following components:
- AvgPleio
The mean of the simulated pleiotropic effect
- CausalEffect
The mean of the simulated causal effect
- StandardError
Standard deviation of the simulated causal effect
- sigma
The value of the residual standard deviation
- CredibleInterval
The credible interval for the causal effect, which includes the lower (2.5%), median (50%) and upper intervals (97.5%)
- samples
Output of the Bayesian MCMC samples
- Priors
The specified priors
References
Bowden et. al., Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. International Journal of Epidemiology 2015. 44(2): p. 512-525. doi:10.1093/ije/dyv080
Examples
if (requireNamespace("rjags", quietly = TRUE)) {
fit <- mr_egger_rjags(bmi_insulin)
summary(fit)
plot(fit$samples)
# 90% credible interval
fitdf <- do.call(rbind.data.frame, fit$samples)
cri90 <- sapply(fitdf, quantile, probs = c(0.05, 0.95))
print(cri90)
}
#> Prior :
#>
#> Pleiotropy ~ dnorm(0, 1E-3)
#> Estimate ~ dnorm(0, 1E-3)
#> sigma ~ dunif(.0001, 10)
#>
#> Estimation results:
#>
#> MCMC iterations = 6000
#> Burn in = 1000
#> Sample size by chain = 5000
#> Number of Chains = 3
#> Number of SNPs = 14
#>
#> Inflating Parameter: 7.63072
#>
#> Estimate SD 2.5% 50% 97.5%
#> Avg Pleio -0.05423754 0.03587126 -0.1249326 -0.05289878 0.01408735
#> Causal Effect 3.74906123 2.12741936 -0.2994558 3.67181831 7.95763439
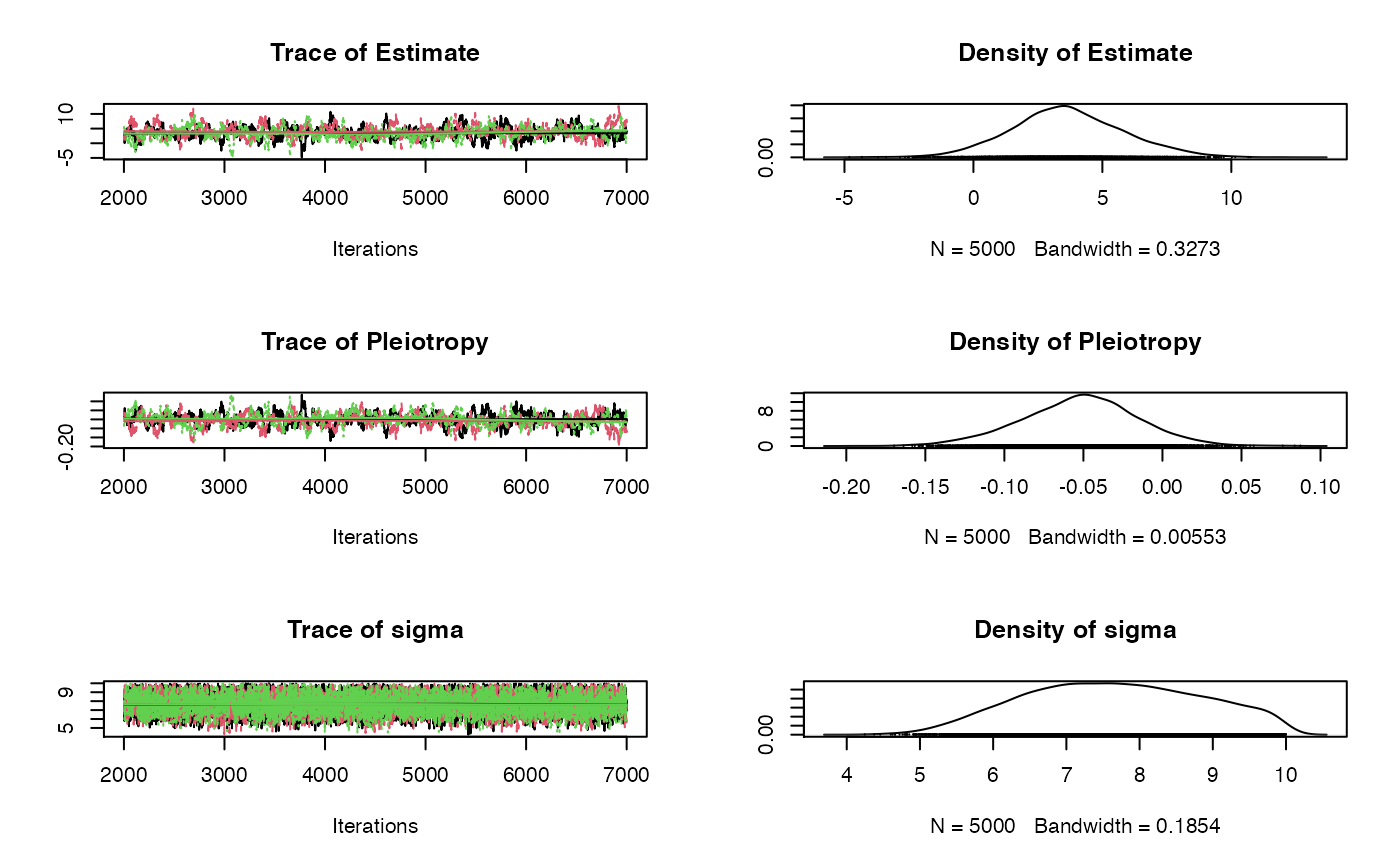 #> Estimate Pleiotropy sigma
#> 5% 0.3637214 -0.114480488 5.686757
#> 95% 7.3196728 0.003112578 9.600718
#> Estimate Pleiotropy sigma
#> 5% 0.3637214 -0.114480488 5.686757
#> 95% 7.3196728 0.003112578 9.600718